Re-published from ANS-035
After just over six years in orbit, Fox-1D, designated as AMSAT-OSCAR 92 (AO-92), likely re-entered the Earth’s atmosphere on February 3, 2024 (Space-Track had not issued the final decay message as of the time of this writing.)

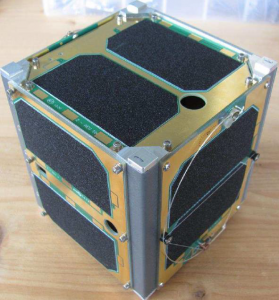
AO-92 was a 1U CubeSat developed and built by AMSAT. It carried a single-channel transponder for mode U/v in FM and also had an L-band converter (the AMSAT L-band downshifter experiment), which allowed the FM transponder to be switched to an uplink in the 23 cm band.
In addition to the transponders, the satellite carried the following scientific and technical payloads:
- High Energy Radiation CubeSat (HERCI) built by the University of Iowa
- Camera Experiment built by Virginia Tech
- MEMS GYRO Experiment built by Penn State-Erie
The satellite had a single whip antenna for the 70 cm and 23 cm bands (uplink), as well as an antenna for the 2m band (downlink).
AO-92 was launched on January 12, 2018 at 03:59 UTC on an Indian PSLV XL rocket, along with the main payloads Cartosat-2F, NovaSAR-S, and 31 other small satellites from the Satish Dhawan Space Center, India. At 05:17 UTC, the antennas were deployed over the North Pole and the satellite began to operate. At 05:28 UTC the first telemetry was received.
On the 03:25 UTC pass on January 26, 2018, AMSAT Vice President – Engineering Jerry Buxton, N0JY, announced that AO-92 had been commissioned and formally turned the satellite over to AMSAT Operations. AMSAT Vice President – Operations Drew Glasbrenner, KO4MA, then declared that AO-92 was open for amateur use.

Rick Behma, VE4AMU, working AO-92 in Mode L/v with a Kenwood TM-941 mobile transceiver and Comet CYA-1216E yagi crossed with 2 meter Arrow II elements.
In addition to a very popular U/v transponder, the satellite provided a couple of unique capabilities. First was the L-band downshifter experiment, which was generally activated for 24 hours each Sunday while the satellite was able to support it. Pre-launch estimates suggested that approximately 100 watts ERP would be required to access the satellite, but much lower power outputs proved to be usable. Many stations operated through the satellite with radios such as the Alinco DJ-G7T at 1 watt of output into handheld antennas of between between 10 and 16 elements. At least one station reported accessing the satellite with just a simple whip antenna on 23 cm.
The camera, developed by students at Virginia Tech, also proved to be popular and delivered many good pictures, with the last photos received on September 19, 2020. An archive of all of the photos captured by ground stations can be found at https://www.amsat.org/tlm/showImages.php?id=4.

The distance record on AO-92’s U/v mode was 5,011 km – a transatlantic QSO between F4DXV and VE1VOX that took place on August 10, 2020. The record via the L/v mode was 4,202 km between OA4/XQ3SA and XE1MEX on June 3, 2020.
By early 2021, the aging NiCd cells – having been purchased in the early 2010s along with the rest of the Fox-1 battery cells – had degraded to the point where the satellite was entering safe mode on every eclipse. It was rarely operational in recent months. The transponder was occasionally turned on, but usually defaulted into “Safe Mode” at the next eclipse. The last telemetry frame was received from the satellite on October 27, 2023 at 01:36 UTC.
By every measure, AO-92 was a tremendously successful amateur radio satellite, providing educational and research benefits to AMSAT’s university partners, as well as providing several years of reliable FM communication for amateurs. Its useful life far exceeded the average operational lifespan for commercial or educational CubeSats.
[ANS thanks Joe Fitzgerald, KM1P, AMSAT Orbital Elements Manager, and Paul Stoetzer, N8HM, AMSAT Executive Vice President, for the above information]